Glossary A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Perched Groundwater Body
A volume of groundwater, in an impermeable basin, at a permanently higher level than the surface of a waterway.
Pesticide
(See Phytosanitary Products)
Phytosanitary Products
A substance used to fight the animal and plant parasites which attack crops: herbicides fight weeds, fungicides fight fungus, insecticides fight insects and rodenticides fight rodents. There are several hundreds of different substances available.
Piezometer
A piezometer is an unused borehole which enables the level of groundwater at a given point on the body to be measured. This level, which varies with use, provides information about the aquifer’s production capacity.
A water point can be used to find out about the resource’s quantitative status. In that case it is equipped with a piezometry measuring unit: a piezometer. This is an access point to the groundwater body (borehole, well, piezometer) via which the level of the body or the hydraulic head, using an instrument (manual probe, water level recorder, digital recorder, which may be remotely transmitted) can be measured.
In the strict sense of the term, a piezometer is a device used to measure the piezometric head at a given point on an aquifer system. This indicates the pressure at this point, enabling the measurement of the unconfined water level or a pressure reading to be recorded (G.Castany, J.Margat (1977) Dictionnaire français d’hydrogéologie).
The piezometer concept has been extended to cover all artificial (wells, boreholes, gravel pits) and natural (potholes, caves) points which provide access to groundwater.
Each piezometer is allocated a national number. This corresponds to the BSS file code linked to the BSS designation (see National Code).


Piezometric Level
Level reached by the water at a point and at a given moment of time in a tube reaching down to the body. It can be transferred onto a piezometric map. Some unused boreholes are used to measure this level. These are called piezometers. This measurement of the body’s level should not be likened to a measurement of water reserves, and the technical characteristics of the installation, the geographical sector, the geological context, and pluviometry should be taken into account when interpreting it.
This level corresponds to the body’s pressure, and is generally given in metres NGF in France.
When this level exceeds ground level, the body is called an artesian body: the water is then spurting up.
The piezometric maps established using all the measured data, give a graphical representation of the surface of groundwater bodies, and enable their progression over time to be monitored and to identify their runoff direction.
Piezometric Time Series or Piezometric Graph
The piezometric time series shows how the level of a monitored body of water or piezometric level has developed over time (see piezometric level). It is made up of measurements linking the level of the body of water to a given date. Depending on the variability of the level of the body of water, measurements are taken more or less frequently.
Measurements obtained are positive or negative in relation to the measuring mark. They are positive when the level of the body of water is below that of the measuring mark (most frequent scenario). They are negative when the opposite scenario occurs (Artesian wells).
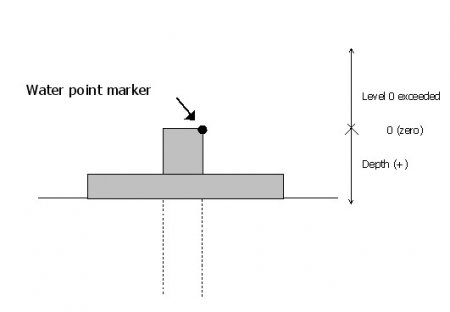
Artesian: a borehole is artesian if the water spurts from it.
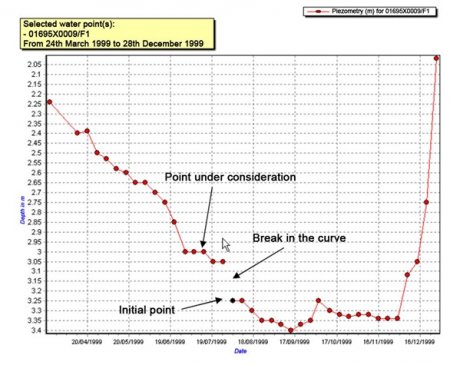
A time series is represented by a curve which is discretised in order to be stored in a succession of points, with each point representing the level of the body of water at a given moment.
The points are linked to each other using a code which indicates whether the point is connected to the previous point in time. If the point is not linked, it constitutes an initial point on a new section of the time series. The presence of an initial point is also symptomatic of a lack of information about the level of the body of water during the period between the initial point and the previous point.
Piezometric Value
(See Piezometric Level)
Pressure Drop (or reduction, fall, decrease, trough)
A temporary or permanent drop in the piezometric level (see piezometric level) of groundwater caused by a natural or artificial alteration (abstraction, drop in supply, linking of aquifers).
Programme of Measures
A River Basin District level document including measures (actions) to be carried out in order to achieve the objectives set out in the revised SDAGE (Blueprint for Water Development and Management), including the WFD environmental objectives. The measures are concrete steps combined with a timescale and a financial evaluation. The steps may be of a regulatory, financial or contractual nature. The programme of measures includes:
- The basic measures, which are the minimum requirements to respect, starting with the application of the current Community and national water protection legislation. Article 11 and Annex VI of the WFD list the basic measures.
- Supplementary measures, encompassing any measures taken in addition to the basic measures in order to meet the WFD’s environmental objectives. Annex VI of the WFD provides a non-exhaustive list of these measures which can be of different types, including legal, economic, fiscal and administrative.
Protection Area
The officially protected space around abstraction points used for drinking water supply, based on the opinion of an accredited hydro-geologist. Non-industrial, agricultural and industrial activities and construction are all banned from the area or regulated, in order to preserve the water resource by avoiding chronic or accidental pollution. From a regulatory standpoint there are three types of areas:
- The immediate protection area for which there are major constraints (activities are banned).
- The nearby protection area in which activities are restricted.
- The more distant protection area which guarantees the continuity of the resource.
Public Interest (see DUP)
The State confers an advantage (state approval due to being of public interest) or imposes a constraint (public interest easements, public interest compulsory purchase order).
Public Interest Declaration (DUP)
(See also DUP, Public Interest)
An official document acknowledging the public interest of an operation planned by a public entity or on its behalf, after having consulted the local population following a public interest enquiry.
This document must be obtained before a compulsory purchase (for public interest reasons) which is necessary in order to continue the operation.





